
Gene Editing for Developing GM Spicy Tomatoes
January 16, 2019| |
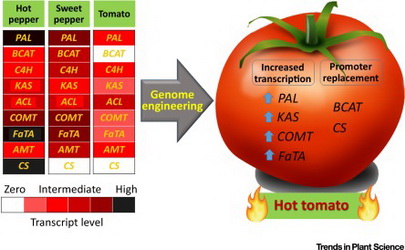 With the development of gene editing tools, experts from the Federal University of Viçosa in Brazil explored on the possibility of engineering spicy tomatoes. The paper is published in Trends in Plant Science.
With the development of gene editing tools, experts from the Federal University of Viçosa in Brazil explored on the possibility of engineering spicy tomatoes. The paper is published in Trends in Plant Science.
The primary goal of developing spicy tomatoes was to easily mass produce capsaicinoids, which are secondary metabolites that give chilli peppers their spicy flavor and has been proven to have health benefits and industrial applications. According to the researchers, two genome editing techniques could be used together to turn on the capsaicinoid biosynthesis in tomato. The first one is the transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs), a set of proteins secreted by pathogenic bacteria, Xanthomonas spp., when they infect plant hosts. Rapid assembly of the TALE genes into a single T-DNA vector would allow simultaneous upregulation of the expression of some key capsaicinoid biosynthesis genes. Actual experimentation would further exhibit whether the transcript levels achieved will be enough for the capsaicinoid pathway to be functional.
The second technique is the use of genome engineering for targeted replacement of promoters. This was proven to be effective in tomato using a constitutive 35S promoter inserted in ANT1 gene, which encodes a transcription factor involved in regulating anthocyanin production. Promoter regions of the inactive genes in the capsaicinoid pathway could be replaced with endogenous tomato fruit-specific promoters to produce cisgenic plants with transcriptionally active genes. Actual testing will reveal if the products are fully functioning, biochemically active, and catalyze the right reactions.
Read the article in Trends in Plant Science.
| |
Biotech Updates is a weekly newsletter of ISAAA, a not-for-profit organization. It is distributed for free to over 22,000 subscribers worldwide to inform them about the key developments in biosciences, especially in biotechnology. Your support will help us in our mission to feed the world with knowledge. You can help by donating as little as $10.
-
See more articles:
-
News from Around the World
- Blueprint for Plant's Immune Response has been Found
- Scientists Identify How Plants Sense Temperature
- Research Finds Extreme Opponents of GM Foods Know the Least but Think They Know the Most
- NRGene and Toyota Decode Strawberry Genome to Develop Better Varieties
- Approval of Monsanto's GM Cotton Seed Patent to Boost India's Biotech Industry
- Mechanism Behind Plant Memory has been Unraveled
- Improved Crops Can Double Agricultural Production in Europe
- EFSA: GM Maize (MON 89034x1507xMON 88017x59122xDAS-40278-9) and Soybean (A2704-12) are Safe for Release
-
Research Highlights
- Rice Plants Engineered for Better Photosynthesis Make More Rice
- Meta-analysis of Soil Enzymatic Responses to Bt Crops
-
Beyond Crop Biotech
- Gene-edited Tilapia Not Classified as GMO in Argentina
- Biotechnology to Possibly Address Forest Health Problems
-
Resources
- Bt Brinjal: The Bangladesh Experience
-
Plant
- Scientists Report Functionally Diverse Type V CRISPR-Cas Systems
- Gene Editing for Developing GM Spicy Tomatoes
-
Read the latest: - Biotech Updates (February 11, 2026)
- Gene Editing Supplement (January 28, 2026)
- Gene Drive Supplement (February 22, 2023)
-
Subscribe to BU: - Share
- Tweet
