Experts Highlight Hybrid Foods as Meat Alternatives
October 1, 2025| |
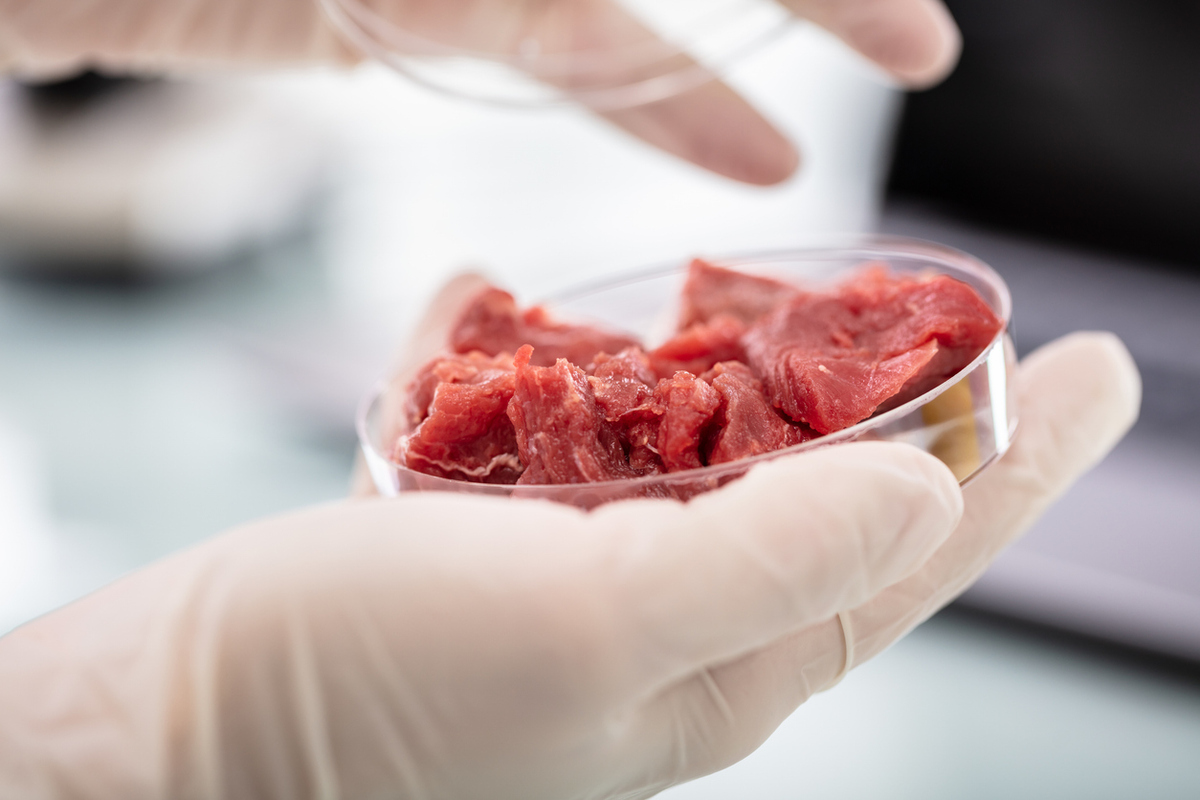
Experts from Tufts University and the University of Massachusetts say that hybrid foods combining proteins from plants, fungi, insects, microbial fermentation, and cultivated meat could deliver nutritious and sustainable alternatives to animal products. According to their study published in Frontiers in Science, this approach could help reduce reliance on industrial livestock while meeting consumer demand for flavor, texture, and health.
The researchers said that by blending different protein sources, hybrids can overcome individual drawbacks, such as costly production and a lack of meat flavor and texture. In the short term, they noted that plant–mycelium hybrids are the most practical option, as they are scalable, nutritious, and already present in commercial products. In the longer term, plant–cultivated meat hybrids may become a better option once production costs decline and expand production capacity.
“Hybrid foods could give us delicious taste and texture without breaking the bank or the planet,” said Prof. David L. Kaplan of Tufts University. However, they also identified hurdles and barriers in mainstreaming hybrid food, including high production costs, regulatory gaps, and consumer skepticism. The research team recommends the optimization of protein sources, scaling up production, environmental and economic impact assessment, and the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to explore new hybrid combinations and processing methods.
For more information, read the article or study from Frontiers in Science.
| |
You might also like:
- A Non-allergenic Wheat Protein Improves the Growth of Cultivated Meat
- Researchers Review the Impact of Animal Proteins in Plants
- Experts Say Effective Communication Can Promote Consumer Acceptance of Cultured Meat
Biotech Updates is a weekly newsletter of ISAAA, a not-for-profit organization. It is distributed for free to over 22,000 subscribers worldwide to inform them about the key developments in biosciences, especially in biotechnology. Your support will help us in our mission to feed the world with knowledge. You can help by donating as little as $10.
-
See more articles:
-
Plant
- Improved CRISPR-Cas Boosts Tomato's Gene Editing Efficiency
- Argentina Approves GM Soybean DBN8205
- USDA APHIS Deregulates GE Insect Resistant Corn
- Bangladeshi Farmers Gain Higher Yields and Profits from Bt Brinjal
-
Food
- Plant-Based Biosensor Could be Key to Timing Fruit Ripening
- Experts Highlight Hybrid Foods as Meat Alternatives
- John Innes Centre and Quadram Institute to Conduct Gene-Edited Tomato Food Trial
-
Environment
- University of Warwick Develops Strategies to Boost Protein Production from Engineered Cells
-
Read the latest: - Biotech Updates (February 18, 2026)
- Gene Editing Supplement (January 28, 2026)
- Gene Drive Supplement (February 22, 2023)
-
Subscribe to BU: - Share
- Tweet